Rotation-corrected satellite precise orbit determination method boosts navigation precision for future mega-constellations
KNOXVILLE, TN, August 15, 2025 /24-7PressRelease/ — Precise orbit determination (POD) is vital for satellite navigation, positioning, and timing services, especially as large Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations grow in scale. A new method integrates inter-satellite link (ISL) data with onboard BeiDou-3 (BDS-3) observations to simultaneously determine the orbits of both LEO and BDS-3 Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. The technique addresses the problem of systematic constellation rotation by referencing the coordinate system implied in BDS-3 broadcast ephemerides and applying a rotation correction. Simulations show that this approach reduces LEO orbit errors from over 20 cm to about 1 cm, offering low-latency, high-accuracy solutions without heavy reliance on ground tracking stations.
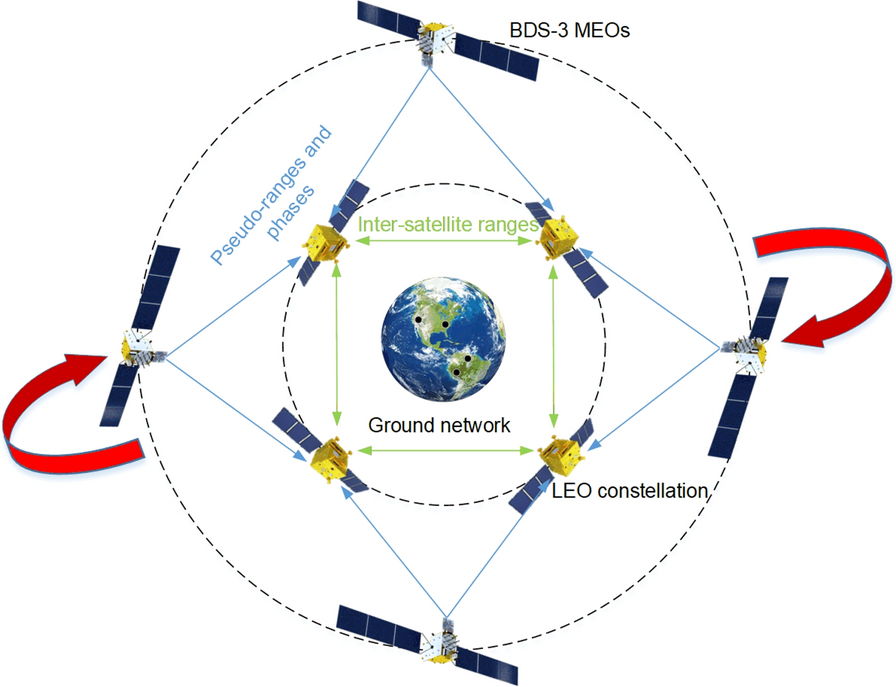
Modern satellite constellations such as OneWeb, Starlink, and CENTISPACETM promise global communications and navigation capabilities using LEO constellations. However, their POD requires dense ground station networks—costly and often limited by geopolitical or geographical constraints. Inter-satellite links (ISLs) help reduce ground dependence but suffer from “rotational unobservability”, where the entire constellation drifts in orientation due to the lack of an absolute spatial reference. Existing fixes often require additional infrastructure or high-quality Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) products, which increase latency and operational complexity. Due to these challenges, a more autonomous, low-latency approach that leverages existing onboard capabilities is needed to ensure reliable, high-accuracy orbits for mega-constellations.
Wuhan University researchers have developed and validated a rotation-corrected integrated POD method that fuses ISL measurements with onboard BeiDou-3 (BDS-3) GNSS observations. Published (DOI: 10.1186/s43020-025-00175-8) in Satellite Navigation on August 4, 2025, the study demonstrates how the technique simultaneously estimates the orbits of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and BDS-3 Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites, corrects systematic rotation using BDS-3 broadcast ephemerides, and achieves centimeter-level precision. The approach significantly reduces reliance on ground stations, making it well-suited for real-time applications in large-scale LEO constellations.
The team simulated a 66-satellite LEO constellation equipped with ISLs and onboard BDS-3 receivers, alongside 24 real BDS-3 MEO satellites. Two processing strategies were tested: one using BDS-3 data from all LEOs, and another from only a subset. In both cases, ISL and GNSS data were jointly processed to form a unified high–low constellation. Due to internal-only measurements, the initial solutions exhibited significant systematic rotation—up to 40 cm cross-track error for LEOs and over 1 m for MEOs. The researchers derived rotation angles between the integrated POD coordinate frame and the BeiDou Coordinate System implied in broadcast ephemerides, then applied a Helmert transformation to correct the orbits. After correction, LEO along-track and cross-track errors dropped from 22.7 cm and 39.3 cm to 1.3 cm and 4.2 cm, respectively. MEO errors fell from over 1.2 m to about 13 cm. Even when only 36 of 66 LEOs carried GNSS receivers, ISL connectivity propagated the correction across the constellation with minimal accuracy loss. Tests also examined the influence of predicted Earth Rotation Parameters and residual errors in broadcast ephemerides.
“This method tackles one of the most stubborn issues in autonomous constellation orbit determination—systematic rotation caused by the lack of absolute spatial reference,” said Dr. Kecai Jiang, corresponding author of the study. “By harnessing readily available BDS-3 broadcast ephemerides and inter-satellite measurements, we can deliver centimeter-level precision without waiting for post-processed GNSS products or building extensive ground networks. This approach is not only efficient but also scalable, paving the way for real-time, high-accuracy navigation services in future mega-constellations.”
The rotation-corrected integrated POD method holds significant promise for global navigation augmentation, autonomous LEO-based navigation systems, and real-time positioning services. By dramatically reducing reliance on ground infrastructure, it enables resilient operations in remote or geopolitically constrained regions. Its scalability makes it ideal for next-generation satellite constellations supporting broadband internet, disaster response, and precision agriculture. Moreover, the ability to achieve near-uniform accuracy across all satellites—even when only part of the constellation carries GNSS receivers—lowers hardware requirements and operational costs. This innovation could become a cornerstone technology for integrating LEO constellations with existing GNSS systems to enhance global navigation and timing performance.
References
DOI
10.1186/s43020-025-00175-8
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43020-025-00175-8
Funding information
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 42204020, 42030109), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2021M702507).
About Satellite Navigation
Satellite Navigation (E-ISSN: 2662-1363; ISSN: 2662-9291) is the official journal of Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The journal aims to report innovative ideas, new results or progress on the theoretical techniques and applications of satellite navigation. The journal welcomes original articles, reviews and commentaries.
Chuanlink Innovations, where revolutionary ideas meet their true potential. Our name, rooted in the essence of transmission and connection, reflects our commitment to fostering innovation and facilitating the journey of ideas from inception to realization.
Related Link:
http://chuanlink-innovations.com
—
For the original version of this press release, please visit 24-7PressRelease.com here